Uncovering the Challenges of Supply Chain Management You Didn’t Know About including external risks, high costs, social and environmental concerns, and technological hurdles. Learn strategies to mitigate these challenges effectively.
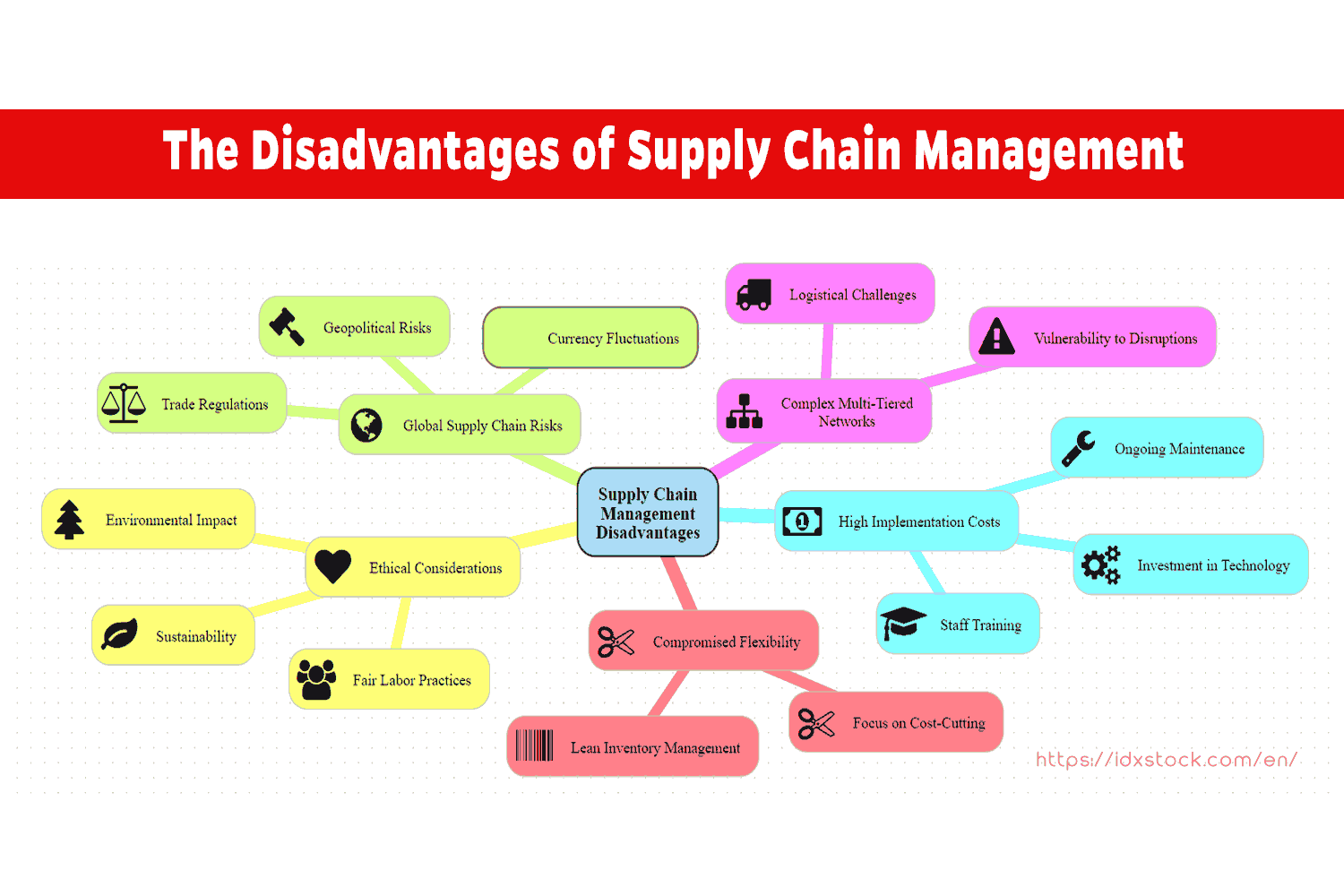
Supply Chain Management (SCM) is essential for optimizing the flow of goods and services, yet it is fraught with challenges. These challenges are interconnected and can significantly impact operational efficiency. This article delves into the major disadvantages of SCM, exploring risks, costs, and other obstacles that companies face.
External Risks and Network Complexity
External Risks
Supply chains are susceptible to various external risks such as political changes, conflicts, geopolitical instability, and shifts in trade regulations. Events like currency fluctuations, natural disasters, or pandemics can disrupt global supply chains, impacting operational continuity. Companies must invest in strategies to mitigate these risks and maintain stability.
Network Complexity
The intricate nature of multi-tiered supply chains adds another layer of complexity. Coordinating and managing these networks require substantial time and resources. The complexity makes it challenging to ensure smooth operations, as every link in the chain must be effectively managed and synchronized.
Costs, Investments, and Flexibility
High Costs
Implementing advanced SCM systems entails significant financial investment in technology and human resources. The continual need for technological upgrades can strain budgets, particularly for smaller companies. Additionally, the pressure to cut costs may lead to sacrifices in other areas such as quality and sustainability.
Flexibility Issues
While focusing on efficiency and cost reduction, companies might compromise flexibility. Lean inventory management, though cost-effective, can heighten vulnerability to disruptions. Balancing cost-efficiency with the ability to adapt to market changes is crucial for maintaining supply chain resilience.
Social, Environmental, and Quality Considerations
Social and Environmental Impact
Supply chain activities often have adverse effects on the environment, such as waste and emissions. Companies must address ethical considerations, including worker rights and sustainable sourcing. Ensuring long-term environmental and social sustainability is critical for positive impacts.
Quality and Reputation
Product quality issues can damage a company’s reputation and result in financial losses. Customer satisfaction heavily relies on a company’s ability to meet quality expectations consistently. Ensuring stringent quality control and adhering to best practices can help mitigate these risks.
Human Factors and Technological Challenges
Skill Gaps and Team Dynamics
A shortage of skills and expertise in managing complex supply chains can lead to errors and inefficiencies. Motivating employees, fostering a positive corporate culture, and improving communication are essential for enhancing team performance and collaboration.
Technological Integration
Integrating various information systems within the supply chain can be challenging. Data flow interruptions and cybersecurity threats pose additional risks. Companies must invest in secure and compatible technology solutions to ensure smooth and secure data management.
Changing Consumer Demands and Financial Risks
Evolving Consumer Preferences
The rise of e-commerce and personalized consumer demands has increased supply chain complexity. Companies must adapt their supply chains to accommodate faster and more flexible order fulfillment while addressing consumer concerns about sustainability.
Financial Challenges
Fluctuating raw material prices and credit risks can impact profit margins and financial stability. Companies need strategies to manage these financial uncertainties and maintain a robust supply chain.
Strategic Approaches
To effectively address these disadvantages, companies should adopt a strategic approach. Analyzing case studies of successful and unsuccessful SCM implementations, conducting industry surveys, and consulting experts can provide valuable insights. Embracing best practices and cutting-edge technologies is essential for building a resilient and efficient supply chain.
Conclusion
Managing the disadvantages of supply chain management requires a comprehensive understanding of the associated risks and challenges. By balancing cost, flexibility, and quality while addressing social and environmental concerns, companies can enhance their supply chain operations. Strategic planning and continuous improvement are key to navigating the complexities of SCM effectively.
Tips and Recommendations:
- Risk Assessment: Regularly evaluate and address external risks to minimize disruptions.
- Invest Wisely: Prioritize investments in technology and training to maintain an efficient SCM system.
- Focus on Sustainability: Incorporate ethical and sustainable practices to enhance environmental and social impact.
- Enhance Skills: Develop and retain skilled personnel to improve supply chain management.
- Stay Flexible: Adapt to changing consumer demands and market conditions to remain competitive.
By incorporating these strategies, companies can better manage the inherent challenges of supply chain management and achieve operational success.
